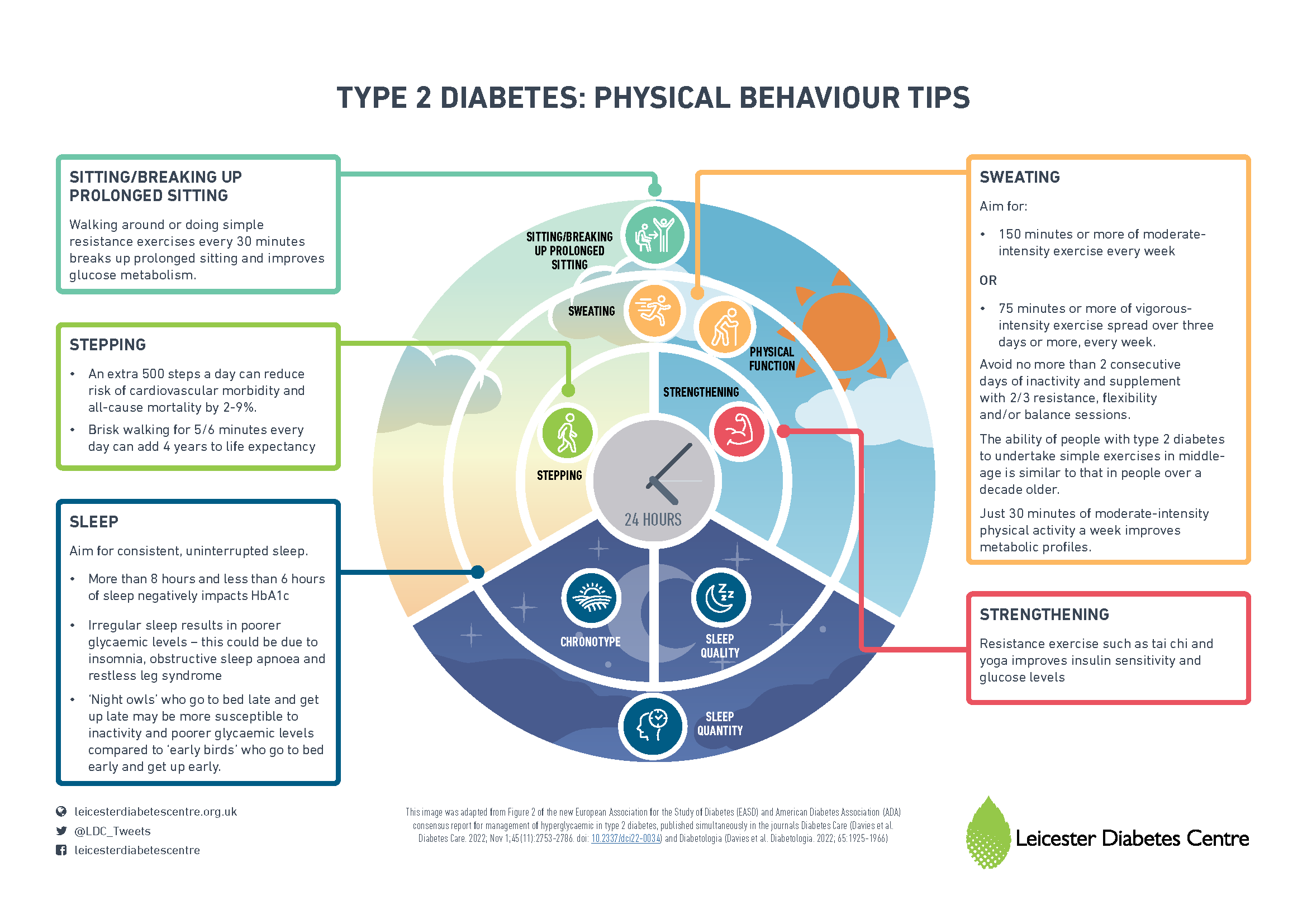
Want to take control of your diabetes? Diabetes management is the key!
Diabetes management is the ongoing process of taking care of yourself if you have diabetes. This involves monitoring your blood sugar levels, eating a healthy diet, getting regular exercise, and taking medication if necessary. Diabetes management can help you avoid or delay the development of serious complications, such as heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, and blindness.
There are many different aspects to diabetes management, but the most important thing is to work with your doctor or diabetes care team to create a plan that is right for you. This plan will include specific targets for your blood sugar levels, as well as recommendations for diet, exercise, and medication. It is also important to monitor your blood sugar levels regularly and to make adjustments to your plan as needed.
Read also:Unveiling The Secrets Of The February 7 Zodiac Your Personality Unveiled
Diabetes management can be challenging, but it is essential for living a long and healthy life with diabetes. By following your doctor's recommendations and making healthy choices, you can take control of your diabetes and reduce your risk of complications.
Here are some of the benefits of diabetes management:
- Lower blood sugar levels
- Reduced risk of heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, and blindness
- Improved quality of life
- Increased life expectancy
If you have diabetes, talk to your doctor or diabetes care team about creating a diabetes management plan that is right for you.
Diabetes Management
Diabetes management encompasses various essential aspects that contribute to the overall well-being of individuals with diabetes. These key aspects, ranging from monitoring to lifestyle modifications and medical interventions, play a crucial role in managing blood sugar levels and preventing complications.
- Monitoring: Regular blood sugar monitoring is vital for understanding blood glucose patterns and adjusting treatment plans accordingly.
- Medication: Insulin or other medications may be prescribed to regulate blood sugar levels, depending on the type and severity of diabetes.
- Diet: Maintaining a healthy diet, including balanced nutrition and limiting sugar intake, is essential for managing blood sugar levels.
- Exercise: Regular physical activity helps improve insulin sensitivity and lower blood sugar levels.
- Education: Ongoing education about diabetes, its management, and potential complications empowers individuals to make informed decisions.
- Support: Access to support groups, healthcare professionals, and family can provide emotional and practical assistance.
These key aspects are interconnected and interdependent. Effective diabetes management requires a comprehensive approach that addresses each of these elements. By adhering to medication regimens, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, monitoring blood sugar levels, and seeking support when needed, individuals with diabetes can optimize their health outcomes and live fulfilling lives.
1. Monitoring
Regular blood sugar monitoring is a cornerstone of effective diabetes management. By tracking blood glucose levels throughout the day, individuals can gain valuable insights into how their bodies respond to food, exercise, and medication. This information empowers them to make informed decisions and adjust their treatment plans as needed, ultimately optimizing blood sugar control and reducing the risk of complications.
Read also:Ultimate Guide To Rogers Arena Seating Find The Best Views
For instance, if blood sugar levels are consistently high after meals, an individual may need to adjust their diet or increase their medication dosage. Conversely, if blood sugar levels drop too low, they may need to consume a snack or reduce their medication. Regular monitoring allows for timely adjustments, preventing extreme fluctuations in blood sugar levels and their associated health risks.
Furthermore, blood sugar monitoring provides healthcare providers with objective data to assess the effectiveness of treatment plans and make necessary modifications. This collaborative approach between individuals with diabetes and their healthcare teams ensures that treatment is tailored to individual needs and goals, maximizing the likelihood of successful diabetes management.
In conclusion, regular blood sugar monitoring is an essential component of diabetes management. By providing valuable insights into blood glucose patterns, it empowers individuals to make informed decisions and adjust their treatment plans accordingly. This ongoing monitoring process, in conjunction with the guidance of healthcare providers, is crucial for achieving optimal blood sugar control and preventing the development of diabetes-related complications.
2. Medication
Medication plays a crucial role in diabetes management, particularly for individuals with type 1 diabetes and those with type 2 diabetes who are unable to adequately control their blood sugar levels through lifestyle modifications alone. Insulin, a hormone naturally produced by the pancreas, is essential for regulating blood sugar levels by allowing glucose to enter cells for energy production. In type 1 diabetes, the body does not produce insulin, while in type 2 diabetes, the body either does not produce enough insulin or does not use insulin effectively.
When blood sugar levels are consistently elevated, medication may be prescribed to lower them and prevent or delay the development of serious complications such as heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, and blindness. The choice of medication depends on several factors, including the type and severity of diabetes, individual patient characteristics, and response to previous treatments. Common medications used to treat diabetes include insulin, oral medications such as metformin and sulfonylureas, and injectable medications such as GLP-1 receptor agonists and SGLT2 inhibitors.
Medication adherence is essential for effective diabetes management. Taking medications as prescribed, even when feeling well, is crucial for maintaining blood sugar control and reducing the risk of complications. Healthcare providers work closely with individuals with diabetes to develop personalized treatment plans that include appropriate medications, dosage adjustments, and monitoring strategies to optimize outcomes.
In summary, medication is an indispensable component of diabetes management, particularly for individuals who are unable to adequately control their blood sugar levels through lifestyle modifications alone. Insulin and other medications help regulate blood sugar levels, preventing or delaying the development of serious complications and improving the quality of life for individuals with diabetes.
3. Diet
Diet plays a pivotal role in diabetes management, as it directly influences blood sugar levels. A balanced diet that is low in sugar and rich in nutrients provides the body with the necessary energy and building blocks to function optimally while helping to manage blood sugar levels effectively.
- Carbohydrate Management
Carbohydrates are the body's primary source of energy. However, refined carbohydrates, such as sugary drinks, white bread, and pastries, can cause rapid spikes in blood sugar levels. Conversely, complex carbohydrates, such as whole grains, fruits, and vegetables, release glucose more slowly, providing sustained energy and helping to prevent blood sugar spikes.
- Protein Intake
Protein is essential for building and repairing tissues. Including lean protein sources, such as fish, chicken, beans, and tofu, in the diet can help slow down the absorption of glucose, promoting stable blood sugar levels.
- Fat Consumption
Healthy fats, such as those found in olive oil, avocados, and nuts, can help improve insulin sensitivity and reduce inflammation. However, saturated and trans fats, commonly found in processed foods and red meat, should be limited as they can raise cholesterol levels and increase the risk of heart disease.
- Fiber Intake
Dietary fiber, found in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, helps regulate blood sugar levels by slowing down the absorption of glucose. It promotes satiety, reducing the likelihood of overeating and subsequent blood sugar spikes.
Adhering to a healthy diet that aligns with the principles outlined above is crucial for effective diabetes management. By making informed choices about food intake, individuals with diabetes can maintain stable blood sugar levels, reduce the risk of complications, and improve their overall well-being.
4. Exercise
Regular physical activity is an integral component of diabetes management, playing a crucial role in improving insulin sensitivity and lowering blood sugar levels. Engaging in regular exercise offers numerous benefits for individuals with diabetes, including:
- Enhanced Insulin Sensitivity
Exercise increases the body's sensitivity to insulin, a hormone that facilitates the uptake of glucose from the bloodstream into cells for energy production. Improved insulin sensitivity allows for better utilization of glucose, resulting in lower blood sugar levels.
- Increased Glucose Uptake
Physical activity stimulates the muscles to take up glucose from the bloodstream, even in the absence of insulin. This increased glucose uptake contributes to lower blood sugar levels and promotes energy production.
- Reduced Insulin Resistance
Regular exercise helps reduce insulin resistance, a condition in which the body's cells become less responsive to insulin. By improving insulin sensitivity, exercise makes insulin more effective in lowering blood sugar levels.
- Improved Blood Flow
Exercise promotes better blood flow throughout the body, including to the muscles. This improved blood flow enhances the delivery of oxygen and nutrients to the muscles, facilitating glucose uptake and energy production.
Incorporating regular physical activity into a diabetes management plan is essential for achieving optimal blood sugar control and reducing the risk of complications. Exercise helps lower blood sugar levels, improves insulin sensitivity, and promotes overall well-being, making it a cornerstone of effective diabetes management.
5. Education
Education is a cornerstone of effective diabetes management, empowering individuals to take an active role in their health and well-being. Ongoing education equips individuals with the knowledge and skills necessary to understand their condition, manage their blood sugar levels, and prevent or delay complications.
- Understanding Diabetes
Education provides a comprehensive understanding of diabetes, including its types, causes, and symptoms. Individuals learn about the role of insulin in regulating blood sugar levels and the importance of monitoring their blood sugar regularly.
- Self-Management Skills
Education empowers individuals with the skills to manage their diabetes effectively. They learn about healthy eating habits, the importance of regular physical activity, and how to adjust their insulin or medication dosage as needed.
- Complication Prevention
Education helps individuals understand the potential complications of diabetes and how to prevent or delay their onset. They learn about the importance of regular checkups, eye exams, and foot care, as well as the signs and symptoms of complications such as heart disease, stroke, and kidney disease.
- Emotional Support
Education also provides emotional support to individuals with diabetes. They learn about the challenges of living with a chronic condition and develop coping mechanisms for dealing with stress, anxiety, and depression.
By empowering individuals with knowledge, skills, and support, education plays a vital role in diabetes management. It enables individuals to make informed decisions about their health, manage their blood sugar levels effectively, and reduce their risk of complications, ultimately leading to improved outcomes and a better quality of life.
6. Support
In diabetes management, support plays a crucial role in helping individuals cope with the challenges of living with a chronic condition and achieving optimal health outcomes. Access to support groups, healthcare professionals, and family provides invaluable emotional and practical assistance.
Support groups offer a sense of community and shared experiences. Individuals with diabetes can connect with others who understand their struggles, provide encouragement, and offer practical advice. Healthcare professionals, including doctors, nurses, and diabetes educators, provide medical guidance, monitor progress, and adjust treatment plans as needed. Family members can offer emotional support, practical help with daily tasks, and motivation to adhere to treatment regimens.
The emotional support provided by support groups, healthcare professionals, and family can help individuals with diabetes manage the psychological impact of the condition. Diabetes can lead to feelings of isolation, anxiety, and depression. Support systems can provide a sense of belonging, reduce stress, and improve overall well-being. Practical assistance, such as help with meal planning, medication management, and transportation to medical appointments, can alleviate the burden of diabetes management and promote adherence to treatment plans.
Studies have shown that individuals with diabetes who have access to strong support systems have better blood sugar control, lower rates of complications, and improved quality of life. Support groups, healthcare professionals, and family members can empower individuals to take an active role in their diabetes management, make informed decisions, and live healthier, more fulfilling lives.
FAQs on Diabetes Management
Diabetes management is a complex but essential aspect of living a healthy life with diabetes. Many common concerns and misconceptions surround diabetes management. This FAQ section aims to provide clear and informative answers, empowering individuals to take control of their diabetes and achieve optimal health outcomes.
Question 1: What is the most important aspect of diabetes management?
Answer: Blood sugar monitoring is crucial as it allows individuals to understand their blood glucose patterns and make informed decisions about their treatment plans. Regular monitoring helps prevent extreme fluctuations in blood sugar levels and reduces the risk of complications.
Question 2: How often should I check my blood sugar?
Answer: The frequency of blood sugar monitoring varies depending on individual circumstances and treatment plans. It is generally recommended to monitor blood sugar levels multiple times a day, especially before and after meals, before bedtime, and during periods of physical activity.
Question 3: What is the role of diet in diabetes management?
Answer: Maintaining a healthy diet is essential for managing blood sugar levels. A balanced diet that is low in sugar and rich in nutrients helps prevent blood sugar spikes and promotes overall well-being. Complex carbohydrates, lean protein, healthy fats, and fiber are important components of a diabetes-friendly diet.
Question 4: How does exercise help in diabetes management?
Answer: Regular physical activity improves insulin sensitivity, allowing the body to use insulin more effectively. Exercise also helps lower blood sugar levels, promotes weight management, and reduces the risk of heart disease and stroke, which are common complications of diabetes.
Question 5: What is the importance of support in diabetes management?
Answer: Support plays a vital role in diabetes management. Access to support groups, healthcare professionals, and family provides emotional and practical assistance. Support systems can help individuals cope with the challenges of living with diabetes, provide encouragement, and promote adherence to treatment plans.
Summary: Diabetes management involves various aspects, including blood sugar monitoring, diet, exercise, medication, and support. By understanding these key elements and working closely with healthcare providers, individuals with diabetes can effectively manage their condition, reduce the risk of complications, and live healthier, more fulfilling lives.
Transition to the next article section: For further insights into diabetes management, including tips for healthy eating, exercise, and emotional well-being, explore the following sections of this article.
Diabetes Management
Diabetes management encompasses a multifaceted approach that involves monitoring blood sugar levels, adhering to a healthy diet, engaging in regular exercise, taking prescribed medications, and seeking support from healthcare professionals and support groups. By implementing these strategies, individuals with diabetes can effectively manage their condition, reduce the risk of complications, and live healthier, more fulfilling lives.
Diabetes management is an ongoing journey that requires dedication, self-care, and collaboration with healthcare providers. Embracing a proactive approach to diabetes management empowers individuals to take control of their health, prevent or delay complications, and live life to the fullest. Together, we can strive for a future where diabetes is managed effectively and its impact on individuals and society is minimized.